TRIAC dimmer, a popular choice among dimmer types, is a common device used to control incandescent and halogen lighting in homes. As technology has evolved, TRIAC dimming has also become compatible with LEDs. So what is TRIAC and why choose TRIAC dimming over dimming 0-10V or dimming PWM?
In this guide, we will introduce you the TRAIC knowledge in detail, and you will have an in-depth understanding of the difference between TRIAC and other dimming types.
What Is TRIAC?
TRIAC is the abbreviation of “Triode for Alternating Current”, it is a three-terminal, four-layer, bi-directional semiconductor device. TRIAC consists of two silicon controlled rectifiers (SCRs) in anti-parallel state, which can conduct in both directions and control AC power efficiently and accurately.
TRIAC can be considered a bidirectional thyristor because it can control current in both directions, whereas a thyristor can only control current in one direction.
Unlike other thyristors, TRIAC has no anode or cathode, it works for both polarities, regardless of whether the applied gate signal is positive or negative. While a thyristor can control only half of the cycle, TRIAC controls both halves of the AC waveform. This means that TRIAC can better control low power in AC circuits – rated current up to 50A.
TRIAC consists of three terminals, namely Main Terminal 1 (MT1), Main Terminal 2 (MT2) and Gate Terminal G.
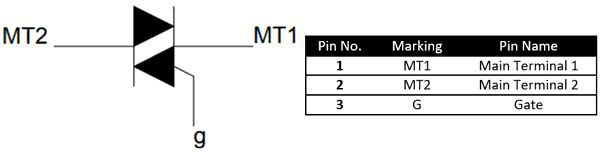
Simply put, in lighting, TRIAC is used to control alternating current to ultimately switch and dim traditional lamps and LEDs.
What Is TRIAC Dimming?
When TRIAC is applied to lighting applications, it is usually called TRIAC dimming. TRIAC dimming is a commonly used lighting control method, which changes the brightness of the lamp by controlling the waveform of the alternating current.
TRIAC dimming usually requires a TRIAC dimmer to achieve, and sometimes you need a TRIAC dimming power supply to control LEDs and LED strip lights.
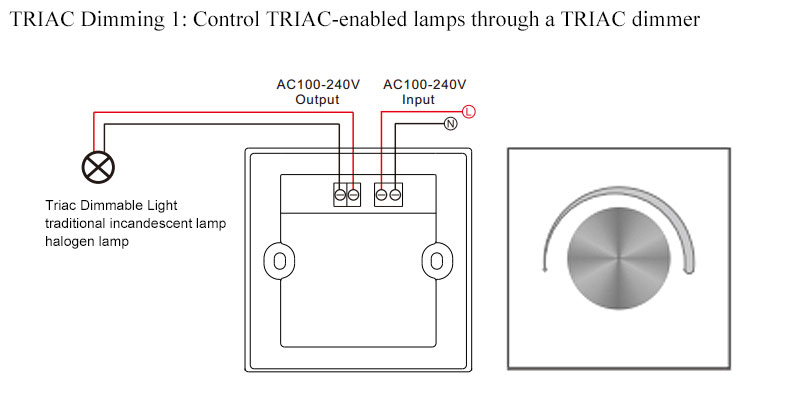
TRIAC Dimming 1: Control TRIAC-Enabled Lamps Through A TRAIC Dimmer
With a TRIAC dimmer, you can adjust the light level of your existing home lighting through a knob or slider to better suit your living needs.
It should be noted that, to directly add a TRIAC dimmer to your lamp, you need to check whether your lamp has a TRIAC device. Traditional incandescent and halogen lamps are directly compatible with TRIAC dimmers.
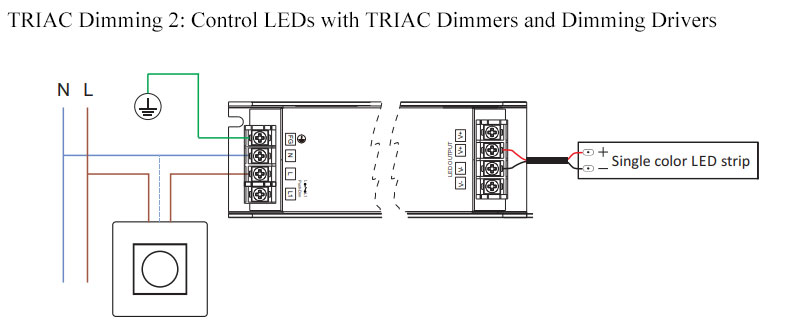
TRIAC Dimming 2: Control LEDs With TRIAC Dimmer And Dimming Driver
As we know, LEDs operate on DC low voltage, while TRIAC works on AC alternating current. So can TRIAC control LED lights and strips?
Now, some well-known LED controller brands like SkyDance have applied TRIAC dimming to LED strip lights. By adding an extra TRIAC dimming driver to the TRIAC dimming system, the high-voltage AC220V is converted into the low-voltage 12V or 24V required by the LED strip to realize the dimming control of LEDs.
What Is A TRIAC Dimmer?
TRIAC dimmer is an electronic device that uses TRIAC to handle high voltage and high current to brighten or dim lights. It is an electrical switch that works by changing the amount of power sent to the light to dim the brightness.
Traditional TRIAC wall dimmers are usually designed in the form of knobs or slider buttons, allowing users to adjust the brightness as needed.
Lutron dimmer switches should be what most people will choose to use. Adding a simple Lutron TRIAC dimmer like CTCL-153P-WH to your home circuit provides brightness control of your lamp.

Modern TRIAC LED dimmers are compatible with WiFi, RF, and other wireless technologies, including a TRIAC dimmer controller and receiver (remote control panel), and can even be operated by a mobile phone APP.
The wireless connection between the TRIAC LED dimmer and receiver reduces the complexity of home wiring design.
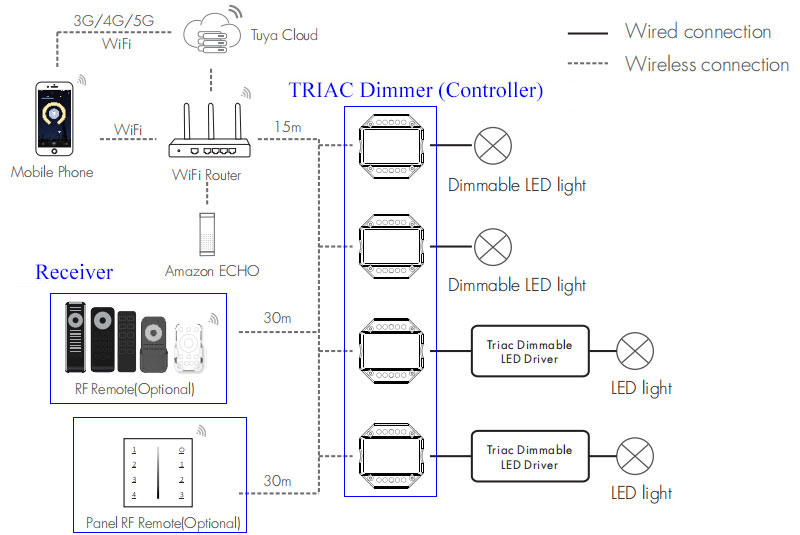
For controlling lighting in large buildings, DMX TRIAC dimmers offer a reliable and efficient solution. Compatible with multiple lighting types such as incandescent, halogen, and some LED lights, these TRIAC dimmers use the Digital Multiplexing (DMX) protocol to enable precise management between lighting control systems, dimmers, and fixtures.
It allows you to independently control individual areas or rooms, and tailor lighting to the specific needs and preferences of each space.
How Does A TRIAC Dimmer Work?
TRIAC dimmer changes the light brightness by controlling the TRIAC switch according to the input of the control signal (dimming knob or smart home control system).
Specifically, TRIAC dimmers chop the AC voltage into many small segments, each of which is half a sine wave. A TRIAC switch is used to time each small segment to control how long and how much voltage the current flows to the bulb, thus changing the lamp brightness.
TRIAC switch is off, the bulb is de-energized and no current flows through it.
TRIAC switch is turned on, current begins to flow to the bulb, causing it to glow.
TRIAC switch is turned on earlier, the electricity takes longer to flow to the bulb and the light is brighter.
TRIAC switch is turned on later, the current has less time to flow to the bulb and the light will be less bright.
Is TRIAC Dimming Good?
TRIAC dimming is a physical dimming that controls the light brightness by adjusting the time and amount of current flowing to the bulb. So it can directly control the bulb brightness without any additional equipment.
However, its dimming range is physically limited and some specific dimming requirements may not be achievable.
In addition, TRIAC dimmers may generate a certain degree of noise and electromagnetic interference. Proper design and protection measures are required to reduce interference.
Advantages of TRIAC Dimming
Low cost. TRIAC dimmers are usually less expensive than other dimmers and are suitable for homes and businesses on a budget.
High precision. TRIAC dimmer can achieve high dimming accuracy and can adapt to different lighting requirements in different scenarios.
Simple wiring circuit. TRIAC dimming uses AC power, no special power supply and wiring are required. (Please mind your safety when operating with AC power)
Disadvantages of TRIAC Dimming
Not suitable for all types of bulbs. TRIAC dimmer usually works with traditional incandescent and some halogen lights, but not with other types of bulbs like LED lights.
Noise and electromagnetic interference. Since TRIAC dimmer uses high-frequency switching, there may be noise and electromagnetic interference that may interfere with other electronic equipment.
Ineffective. During the TRIAC dimming process, some electric energy may be wasted, resulting in reduced energy efficiency.
Should I Choose TRIAC Dimming?
If your home lighting system uses traditional incandescent or halogen lamps, TRIAC dimmer may be a good choice. It can achieve high dimming accuracy at a relatively low cost.
However, if your home lighting system uses LED lights or other incompatible bulbs, you need to consider other dimming types like 0-10V dimming, PWM dimming, or DALI dimming. We’ll talk about Triac dimming, 0-10V dimming, and PWM dimming below.
Your best bet is to check the instructions for the light bulb you are using and contact the manufacturer for the best dimming scheme.
Is TRIAC Dimming Leading Or Trailing Edge?
TRIAC dimming can achieve both leading-edge dimming and trailing-edge dimming, depending on the design and the control method of the dimmer.
Therefore, it is not simple to say that TRIAC dimming is leading-edge dimming or trailing-edge dimming. Different TRIAC dimmers may use different dimming methods.
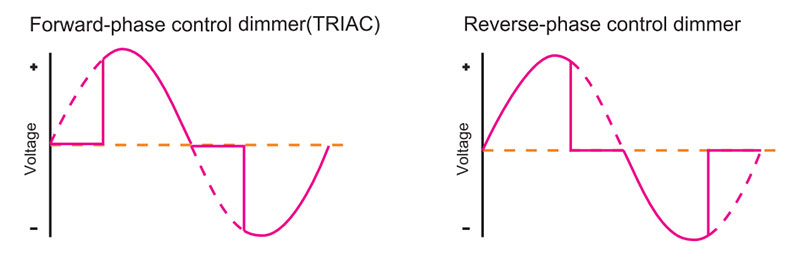
What Is Leading-Edge Dimming?
Leading edge dimming and trailing edge dimming are concepts related to TRIAC dimming. They describe different dimming methods in the positive half-cycle and negative half-cycle.
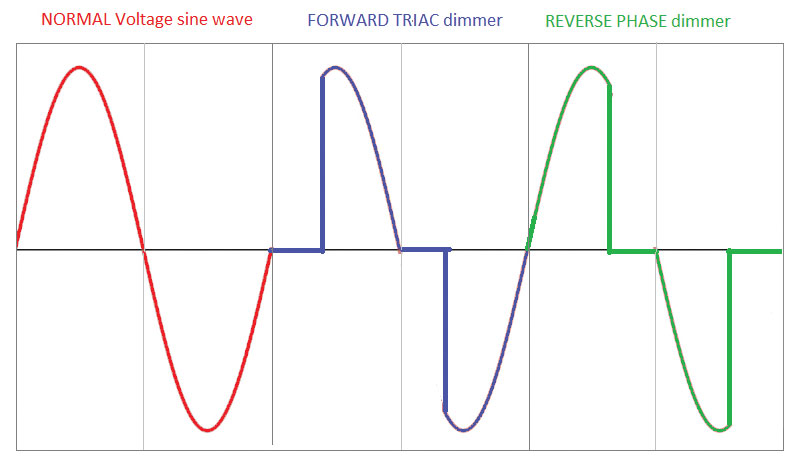
Leading-edge dimming (Forward Phase dimming) refers to starting dimming at the beginning of the positive half-cycle of the alternating current. The current flows into the load lamp within a short period of time after the voltage passes through zero.
In the process of leading-edge dimming, the magnitude of the current gradually increases from zero to realize the gradual lighting of the lamp.
Leading edge dimming is typically used for incandescent bulbs. Every half-cycle generates a rapid voltage, which will cause the current of the light source to increase sharply.
What Is Trailing-Edge Dimming?
Trailing-edge dimming (Reverse Phase dimming) refers to starting dimming at the end of the positive half cycle of alternating current. Cut off the current from the load light for a short period of time before the voltage passes through zero.
During the trailing edge dimming process, the magnitude of the current gradually decreases from the maximum value to realize the gradual dimming of the light.
This type of dimming is usually used with electronic drivers and does not cause a sharp rise in voltage/current to the light source. Similar to ELV (Electronic Low Voltage lighting) dimming.
In both cases, you are achieving dimming by reducing the power output. The more you chop, the darker the light becomes.
TRIAC Dimming vs 0/1-10V Dimming
TRIAC dimming and 0/1-10V dimming are commonly used physical dimming methods, but their working principles and applications are different.
The following table explains the difference between TRIAC dimming and 0-10V/1-10V dimming in detail:
| Type | TRIAC Dimming | 0/1-10V Dimming |
| Definition | Use thyristor TRIAC for dimming | A voltage control dimming method |
| Circuit | AC power (such as light bulbs, motors, etc.) | DC power (such as LED lamps, drivers, etc.) |
| Dimming Principle | TRIAC changes the current and power of the load lamp by controlling the positive half-cycle (leading edge dimming) or negative half-cycle (trailing edge dimming) of the voltage, so as to achieve dimming. | Adjust the current and brightness of the output load by changing the input 0-10V DC voltage. |
| Advantages | Simplicity, stability, low cost | high precision, high reliability |
| Applications | In lighting, electrical appliances, etc. | high-power applications and occasions that require precision dimming, such as lighting control of large buildings, stages, etc. |
| Controlled Lighting System | Small | Large |
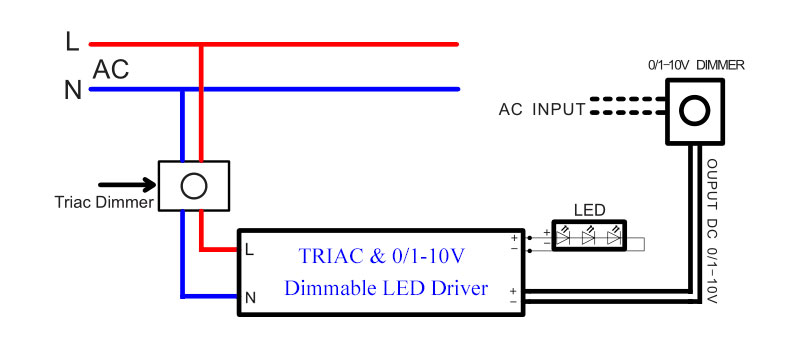
TRIAC & 0/1-10V Dimmable LED Driver
In order to better adapt to different types of dimming requirements and applications in the market, dimmable LED drivers compatible with both TRIAC dimming and 0 to 10 volt dimming have appeared.
Some users may need to use both TRIAC dimming and 0-10 volt dimming in the same lighting system, this meets their needs.
At the same time, TRIAC & 0-10V LED dimmable drivers can better control LED strip lighting. It can choose different dimming methods according to different needs.
For example, in a smaller room, use TRIAC dimming to control the light brightness with a simple TRIAC dimmer switch. In larger rooms or venues, it may be necessary to use a Lutron 0-10V dimmer to achieve more precise dimming control and more uniform lighting effects.
TRIAC Dimming vs PWM Dimming
TRIAC dimming is an analog dimming method, which can smoothly adjust the current signal to achieve a more natural dimming effect. It regulates the current by controlling the TRIAC elements in the circuit.
However, its dimming accuracy is low, and only can achieve simple brightness adjustment.
PWM dimming is a digital dimming method that can achieve more precise dimming effects, especially suitable for lighting scenarios that require precise adjustment like office, residential, and commercial fields.
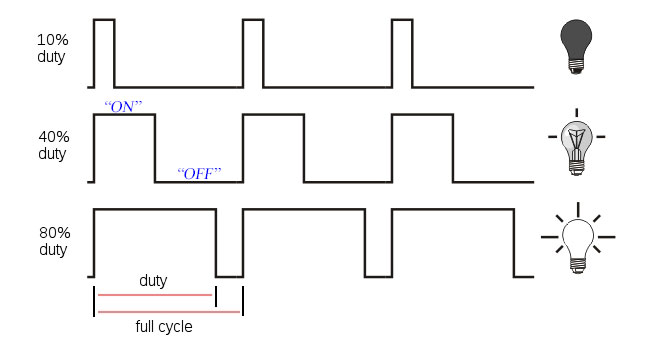
It achieves dimming by controlling the ratio of the power-on time and power-off time of the LED lights. PWM dimming realizes the dimming of LEDs by installing a DC PWM dimmer between the LED strip and the standard power supply.
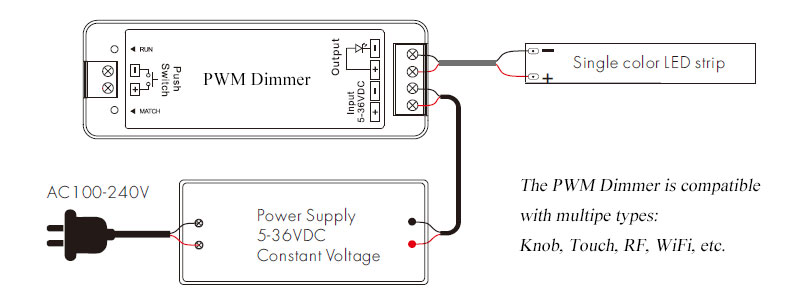
PWM dimming is mainly used for LED lights and light strips, it can precisely control the brightness of LEDs. Due to the fast response speed of the LED, high-frequency PWM dimming can be realized, making the dimming effect more uniform and stable.
At the same time, when using PWM dimming, it is necessary to select a high-quality LED power supply and dimmer to ensure the stability and reliability of the dimming effect.
Compared with TRIAC dimming, PWM dimming has the following advantages and disadvantages:
- Advantages: Precise brightness adjustment; High efficiency; Low noise; Wide range of applications;
- Disadvantages: Expensive; More hardware support is required (Circuits and controllers that support PWM dimming); There may be flickering problems.
| Type | TRIAC Dimming | PWM Dimming |
| Definition | Analog dimming method | Digital dimming method |
| Circuit | AC power | DC power |
| Dimming Principle | Regulate current by controlling the TRIAC elements | Control the ratio of the power-on time and power-off time of LED lights |
| Advantages | Simplicity, Low cost | Precise brightness adjustment, High efficiency, Low noise |
| Applications | Traditional lights | LED lights |
TRIAC & 0-10V & 1-10V & PWM Dimmable LED Power Supply
TRIAC dimming, 0-10 dimming, and PWM dimming, if you like them all, how do you choose? I’m happy to tell you that you can use these methods together to dim LED lights, and only need a dimmable power supply.
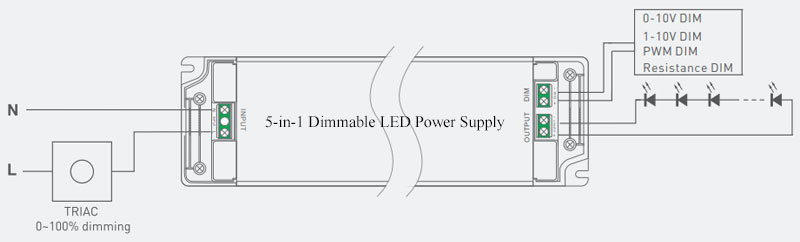
If you need to use different dimming methods to control LED lights, using a 5-in-1 dimmable LED power supply compatible with multiple dimming methods is a very good choice.
This 5-in-1 LED dimming power supply can achieve a more stable and consistent brightness output, avoiding the problem of unstable brightness caused by different dimming methods.
And this 5-in-1 dimming power supply simplifies the circuit design, avoiding the use of multiple different dimming power supplies brought about by the complexity of the installation.
If you need to design and install multiple LED light strips, using a dimming power supply compatible with multiple dimming methods can greatly simplify your design work.
The use of LED dimming power supply that is compatible with a variety of dimming enhances the interchangeability between different brands and models of LED lighting equipment, improving the compatibility and interchangeability of equipment.
If you need to use different brands or models of LED lighting equipment, the use of this dimming power supply can ensure their compatibility.
What Is Dimming Curve?
The dimming curve is a curve describing the relationship between the dimming brightness output and the input control signal. Different types of dimming methods have different dimming curves.
For example, TRIAC dimming and 0/1-10V dimming usually use a linear dimming curve, while PWM dimming uses a non-linear dimming curve. This means that when using different dimming methods, the way the light brightness changes will also be different.
Knowing the dimming curve can help you better choose the dimming method that suits your lighting scene. And avoid the problem of poor or unstable lighting effects caused by using inappropriate dimming methods.
TRIAC dimming uses sine wave voltage to control brightness, so the dimming curve is a curve similar to sine wave, which is softer.
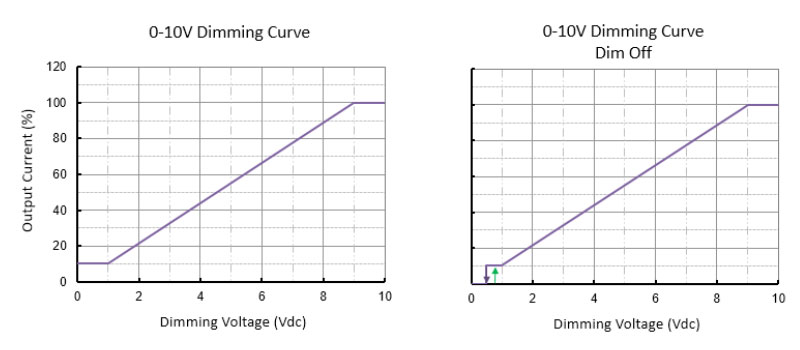
The dimming curve of dimming 0-10V is usually linear, which can provide a relatively smooth dimming effect.
PWM dimming is to control the brightness by quickly switching the LED current, so the dimming curve is a trapezoidal wave, and problems such as flickering may occur.