SK9822, APA102, APA107, HD107, HD107s, and HD108 are all models of LED IC chips that are widely used in addressable LED strip applications. All of these chips use the transmission of data signals with clock signals to achieve lighting control. However, despite their similarity in working principles, they may have some important differences in some aspects. Now, let’s start exploring the differences between SK9822, APA102, APA107, HD107S and HD108!
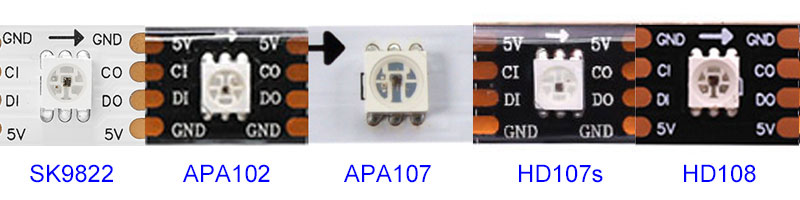
SK9822, APA102, APA107, HD107, HD107S, and HD108 Overview
APA102: APA102 is a clone and upgrade of ws2812 LED, which was called “Super LED” at that time. With a 5V working voltage, APA102 refresh rate can reach 19KHZ, transmission rate can reach 30mHZ. But from 2016, the original factory no longer produces APA102 LED chips. So now only the APA102 clone – APA102C exists in the market. But its refresh rate and transmission rate are far worse than APA102.
APA102C 5050 Datasheet
APA102C 2020 Datasheet
SK9822: SK9822 is similar to APA102, it is usually regarded as an improved version or clone of APA102, with similar functions and performance. SK9822 is a more cost-effective product, however, the parameters of SK9822 are much lower, the refresh rate is only 4.7KHZ, and the transmission rate is only 15mHZ, only enough for general applications. The operating voltage is 5 volts.
SK9822 Datasheet
APA107: APA107 provides similar functionality to APA102, but it uses a slightly different communication protocol than APA102. APA107 introduces a controllable PWM pin for improved color control accuracy and is designed to be more compatible with some microcontrollers. The APA107 operates at 5 volts and has a PWM frequency of 9 kHz.
APA107 Datasheet
HD107 and HD107s: HD107 is similar to APA107, but with better color performance and higher overall quality. HD107S LED is a direct replacement for the Taiwan APA102 LED, which uses Newstar’s NS107S IC. HD107s takes some of the control features of APA102 LED chip and further enhances pin stability and the factory quality inspection process. They operate on 5 volts with a PWM frequency of 30 kHz.
HD107S Datasheet
HD108: The HD108 is an upgraded version of the HD107S, delivering improved color rendering and stability. Operates at 5 volts with a PWM frequency of up to 50 kHz. It is the newest chip in the HD series and offers enhanced functionality. HD108 shows the best animation and visual effects, and is ideal for LED screens and outdoor advertising displays that require high image quality and brightness control.
| LED IC Chip | PWM Refresh Rate | Max. Transmission Speed | Gray Scale | LED Type | LED Color | Working Voltage | LED Density (/m) |
| SK9822 | 4.7KHz | 15MHZ | 8-bit 256 | 5050 | RGB | 5V | 30, 60, 72, 144 |
| APA102 | 20KHZ | 20MHZ | 8-bit 256 | 2020, 5050 | RGB, White | 5V, 12V | 30, 60, 144 |
| APA107 | 9KHZ | 30MHZ | 8-bit 256 | 5050 | RGB, White | 5V | 30, 60, 96, 144 |
| HD107 | 26+ KHz | 40MHz | 8-bit 256 | 5050 | RGB | 5V | \ |
| HD107s | 27KHZ | 40MHZ | 8-bit 256 | 5050 | RGB, White | 5V | 30,60, 96,144 |
| HD108 | 27KHZ | 40MHZ | 16-bit 65536 | 5050 | RGB, RGBCCT | 5V | 30, 60,96, 144 |
APA102 vs SK9822 vs WS2812 vs SK6812
APA102 and SK9822 use a two-wire communication protocol where one wire is used for data (DAT) transmission and the other for clock (CLK) signaling. This protocol allows for more precise control of each LED in a strip light or matrix.
WS2812 and some SK6812 use a one-wire communication protocol that combines the data and clock signals on a single wire, simplifying wiring but potentially limiting data transfer rates. And the refresh rate of the WS2812 may not be as high as that of the APA102 and SK9822 in some cases.
APA102 and SK9822 are more robust and reliable than WS2812 and SK6812 because of their inherent data interlock.
So, APA102 and SK9822, which one is best?
SK9822 is compatible with APA102. A significant difference between APA102 and SK9822 is their PWM refresh rate. APA102 has a PWM frequency of 20kHz, while SK9822 operates at a lower frequency of 4.7kHz. This may affect the smoothness and quality of the color transition in some applications.
However, in terms of price, SK9822 is usually more affordable than APA102. The smaller chip size (0.65mm², APA102-1mm²) allows SK9822 to potentially save on production costs.
*Warm Tip: Nowadays the claimed APA102 led strips in the market actually use APA102C ICs.
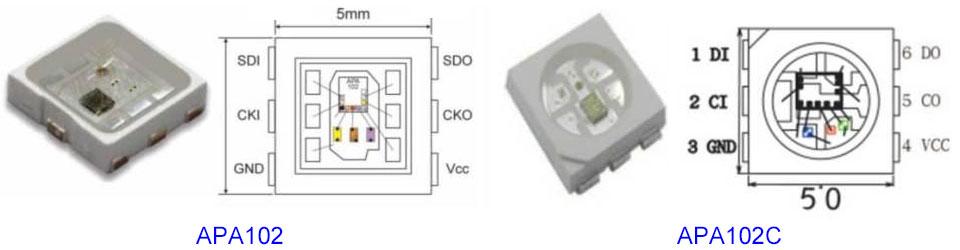
APA104 vs APA106 vs APA102 vs APA107
APA104 is one of the earliest integrated circuits in the APA family, it utilizes a three-wire communication protocol (DAT, CLK, and LAT) with separate lines for data, clock, and latch signals. The additional latching signals are used to update the color data of LEDs, so APA104 is slightly more complicated about wiring than APA102, and it may affect the compatibility with some setups.
APA106 is another early member of the APA family, it uses a two-wire communication protocol (DAT and CLK), similar to APA102. However, APA106 may have limited functionality compared to newer variants such as APA102 and APA107. Newer APA chips may have added more features such as better color depth, higher color accuracy, color correction, compatibility, etc. to make them suitable for professional lighting applications.
APA102 was introduced after APA104 and APA106. APA107 was introduced last, and it uses a slightly different communication protocol to provide similar functionality while enhancing compatibility with specific microcontrollers.
So what is the difference between APA102, APA107, HD107s led strip?
APA107 has similar applications to APA102 and can be used as a suitable replacement, especially if a specific microcontroller is used for compatibility.
HD107S is suitable for applications requiring higher refresh rates and better color consistency. It is the preferred choice in projects where superior performance and reliability are required.
HD107 vs HD107S vs HD108
APA107, HD107S, and HD108 are the same protocol as APA102 and they can directly replace APA102. While HD107 is a solid choice for the need for precise control and good color accuracy, the higher versions of HD107S and HD108 still beat out the HD107 in a few areas.
With higher refresh rates and color consistency than HD107, HD107S and HD108 ensure smoother animation, more responsive lighting effects, and better color matching and uniformity across the entire LED strip or pixel matrix. Therefore, HD107S and HD108 are the top choices for projects that require superior performance and faster updates.
One special feature of HD107S is its ability to digitally control the current of the connected LEDs. This means that it is possible to control the LED brightness by varying the current, rather than the traditional control of varying the PWM signal. With 5-bit global current control, you can reduce the brightness of the HD107S LEDs as needed without sacrificing resolution (i.e., the number of gray levels).
In general, HD108 is slightly more expensive than HD107 and HD107S, because it with the fastest refresh rate, uses 16-bit 65536 high grayscale, and has a fuller range of colors. HD108 LED is an upgraded version of HD107S LED. In a nutshell, HD108 is arguably the best of these addressable IC chips.
Pixel LED chips with 16-bit (65536 levels) high grayscale on the market today:
- HD108: 27kHz PWM refresh rate, 40Mbps max transmission speed
- APA102-65536: 4kHZ PWM refresh rate, 30Mbps max transmission speed
- SK9826: 4kHZ PWM refresh rate, 30Mbps max transmission speed
Among them, HD108 LED is near to you. We sell RGB 30 LEDs/m, 60 LEDs/m, 96 LEDs/m, 144 LEDs/m and RGB+WW+CW 144 LEDs/m HD108 led strips.
Learn More About HD108
We talked about HD108 having a 16-bit 65536 high grayscale, so what’s the difference between a 16-bit HD108 LED and other pixel IC chips like the 8-bit APA102? We need to know that higher gray levels provide richer, more realistic and detailed images and animations.
16-bit HD108 vs 8-bit APA102
In an 8-bit LED lighting control system, there are 256 different gray levels, from 0 for pure black to 255 for pure white. Such a lighting system produces relatively smooth brightness transitions, but may have grainy brightness steps in darker areas.
In a 16-bit LED light control system, there are 65,536 different grayscale levels, from 0 to 65,535, which allows LED color changes to be made with greater precision and smoother brightness transitions, especially in darker areas where subtle brightness changes can be seen.
With an appropriate addressable LED controller such as BC216, K-1000C, H801SB, H806SB, you can adjust the brightness of each color (red, green, blue) separately for the HD108 LED strip. If you need such a controller, please click here.
High Refresh Rate
HD108 is considered to be the fastest refreshing pixel LED. It responds and updates the LED status faster for a more instantaneous effect when the signal is transmitted to the LED strip.
Smaller voltage drop
Compared to APA102, HD108 has a lower voltage drop. HD108 has been designed with a lower forward voltage drop, so that HD108 LEDs can achieve a specified brightness level at lower voltages, resulting in a lower voltage drop across the LED strip light.
On the other hand, APA102 has a relatively high forward voltage drop. When operating at the same brightness level as the HD108, the higher voltage drop may result in an increased voltage drop across the APA102 LED strip. This is why long APA102 LED strip can fail.
On shorter APA102 led strips, the transmission delay of the clock signal is relatively small. Therefore, with faster clock speeds, short APA102 led strips are able to follow the clock signals well and achieve stable data transmission and lighting effects.
In contrast, long APA102 LED strips cause signal degradation. As the signal transmission distance on the long strip increases, the clock signal and data signal will gradually weaken, resulting in data transmission problems.
Final Words
In this blog, we provide a comprehensive comparison and introduction to the SK9822, APA102, APA107, HD107, HD107s, and HD108 addressable LED chips. By understanding their features and performance and then choosing the one that best fits your specific project requirements.